MLP to MP4Convert MLP to MP4, MLP to MP4 Converter |
 |
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact |
MP4 MP3 Converter converts MLP files to MP4 format. The software is an all in one audio converter that supports more than 100 audio and video files. MP4 MP3 Converter also supports batch conversion, and is full compatible with Vista and Windows 7.
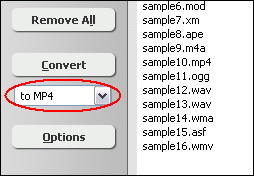
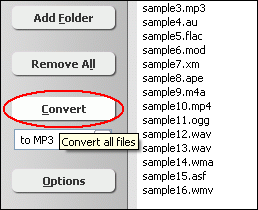
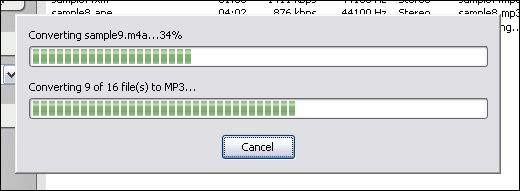
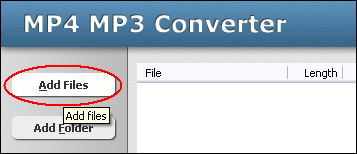 Click "Add Files" button to choose MLP files and add them to conversion list. 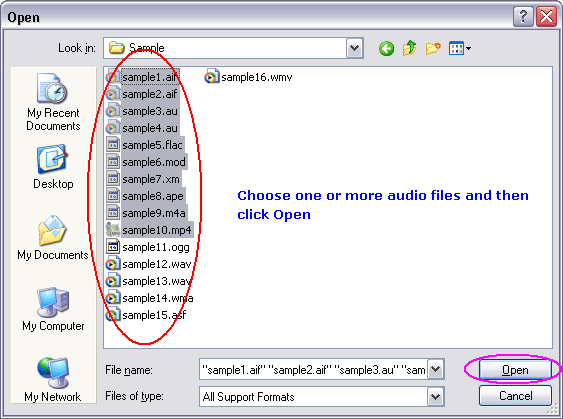 Choose one or more MLP files you want to convert and then click "Open". 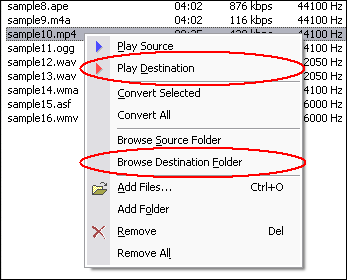 Right-click converted item and choose "Play Destination" to play the destination file, choose "Browse Destination Folder" to open Windows Explorer to browse the destination file. What is MLP? The MLP is used by Meridian codec. Audio compression used on DVD video discs. MLP performs lossless compression of up to 63 audio channels including 24-bit material sampled at rates as high as 192kHz. Lossless compression has many applications in the recording and distribution of audio. In designing MLP we have paid a lot of attention to the application of lossless compression to data-rate-limited ransmission (e.g. storage on DVD), to the option of constant data rate in the compressed domain and to aspects that impact on mastering and authoring. MLP was targeted to provide:
MLP provides for up to 63 channels, but applications tend to be limited by the available data rate. To aid compatibility, MLP uses a hierarchical stream structure containing multiple substreams and hierarchical additional data. With this stream structure decoders need only access part of the stream to playback subsets of the audio. Suitable use of the substreams also allows 2-channel compatibility; a low-complexity decoder can recover a stereo mix from a multichannel stream. Figure 1 gives an overview of the process of losslessly compressing a stream containing multiple audio channels and auxiliary data onto a disc. What is MP4? MPEG-4 is a patented collection of methods defining compression of audio and visual (AV) digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) (ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496 - Coding of audio-visual objects. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of AV data for web (streaming media) and CD distribution, voice (telephone, videophone) and broadcast television applications. MPEG-4 absorbs many of the features of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 and other related standards, adding new features such as (extended) VRML support for 3D rendering, object-oriented composite files (including audio, video and VRML objects), support for externally-specified Digital Rights Management and various types of interactivity. AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) was standardized as an adjunct to MPEG-2 (as Part 7) before MPEG-4 was issued. MPEG-4 is still a developing standard and is divided into a number of parts. Companies promoting MPEG-4 compatibility do not always clearly state which "part" level compatibility they are referring to. The key parts to be aware of are MPEG-4 part 2 (including Advanced Simple Profile, used by codecs such as DivX, Xvid, Nero Digital and 3ivx and by Quicktime 6) and MPEG-4 part 10 (MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 or Advanced Video Coding, used by the x264 encoder, by Nero Digital AVC, by Quicktime 7, and by high-definition video media like Blu-ray Disc). Convert MLP to MP4 Related Topics: FLAC to MP4, XM to MP4, ALAC to MP4, QCP to MP4, ADX to MP4, MMF to MP4, SND to MP4, M4V to MP3, MP4 to WAV, APE to MP4, WMA to MP4, M4A to MP4, M4V to WAV, AIFF to MP4, M4B to MP4, WAV to MP4, SOL to MP4, OGA to MP4, TTA to MP4, MO3 to MP4, GSM to MP4, IT to MP4, SPX to MP4, NSA to MP4, AAC to MP4, W64 to MP4, VOC to MP4, AU to MP4, CDA to MP4, UMX to MP4, S3M to MP4, MP3 to MP4, M4V to M4A, MOD to MP4, F4A to MP4
|
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact | Links |
| Copyright © 2008-2013 Hoo Technologies All rights reserved. Privacy Policy |